CNCA-C11-01 2014 motor vehicle rule
No.:CNCA—C11—01: 2014
IMPLEMENTATION RULES FOR COMPULSORY CERTIFICATION
OF Motor Vehicle
Announced on Aug. 21, 2014 Implemented on Jan. 1, 2015
Certification and Accreditation Administration
0.
Foreword
Based on the safety risk and certification risk of automotive and trailer products, this Rule specifies the basic principles and requirements of implementation of compulsory certification of all the automobile applied, to ensure certification product continually conform with legislation, regulations and standards.
This Rules is supplementary to general implementation rules announced by the Certification and Accreditation Administration of People’s Republic of China (Hereafter “CNCA”), including Implementation Rules for Compulsory Products Certification——Factory Classification, Selection and Determination of Certification Mode, Implementation Rules for Compulsory Products Certification——Utilization of Testing Resources of Factory and Other Certification Results, Implementation Rules for Compulsory Products Certification——General Rules for Factory Inspection.
Accredited certification body should draft implementation specifications according to general implementation rules and this Rules, combining the management of Factory Classification and implement them accordingly at the same time.
A factory should guarantee that its certificated products can continually meet the requirements of certification and applicable standards.
1.
Scope
This Rule is applicable to category M, N vehicles and category O trailers (including complete and incomplete), which are allowed to run on Chinese roads and city streets.
This Rule is not applicable to low speed vehicles (three-wheeled vehicles and low speed trucks), vehicles which run on rails and wheel-specific machinery vehicles designed for working on blocked roads or places not for running on roads, agriculture and forestry tractors, various engineering and machinery and non-cab chassis.
Any modification of scope due to changes of legislation regulation, product standard, and technology and industry policies is subject to the announcements by CNCA.
The application free of certification due to scientific research, testing and other special reasons is subject to the provisions by CNCA.
The Definitions of vehicles refers to GB/T 3730.1 Motor vehicles and trailers-Types-Terms and Definitions; GB/T 17350 Terms and marks in special automobiles and semi-trailers, GB 7258 Technical conditions for safety driving of motor vehicles; the classification of vehicles are in GB/T 15089 Classifications of power-driven vehicles and trailers. For example:
1.1
Complete vehicles: vehicles with expected functions without any manufacture
1.2
Incomplete vehicles: vehicles with expected functions by further manufacture
1.3
Multi-stage manufactured vehicles: vehicles with expected functions through multi-stage certification
1.4
Basic vehicles: Complete vehicles and second-type chassis used in modification
1.5
Components: Component assembly, system, the minimum independent unit of vehicles. For example, lens of wing mirrors assembly, splice in brake hose
1.7
Components: Components and assembly
1.8
System: Combination consisted of components and assembly with specific functions, for example, steering system and braking system
1.9
Second-type chassis: incomplete vehicles which can be complete vehicles with a cargo platform or operation equipment
1.10
Third-type chassis: incomplete vehicles which can be complete vehicles with a can, a cargo platform or operation equipment and integral body
1.11
Mass-produced vehicles: vehicles of mass-production and production of large-scale
1.12
Vehicles of non-mass-production: vehicles of non-large-scale production, the number of year production or import of vehicles covered by each certificate is no more than 500
1.13
Refitted vehicles: vehicles refitted on basis of complete vehicles and second-type chassis Œ
Note 1: Terms and definitions is applicable to this Standard only and can be used together like refitted vehicles of non-mass production, complete refitted vehicles of non-production
3.
Reference Standard for Certification
Factories should implement the standard and provision of automobile product safety, environmental protection, energy saving and prevention of burglary announced by government.
According to this Rules, reference standard for certification refers to Appendix 1.
In principle, only the latest version of the abovementioned reference standards issued by Standardization Administration of China (SAC) should be applied. In case of other versions being needed, announcements on relevant standards made by CNCA should apply.
With the premise of integrity and self-discipline, effective management and stable production, the fundamental certification mode in this Rules is based on fixed safety risk characteristics of products and technology adopted by the majority of factories.
The certification body should, according to the requirements of Implementation Rules for Compulsory Products Certification——Factory Classification, Selection and Determination of Certification Mode, properly manage the classification of its manufacturers and determine the applicable certification mode for each of them.
The fundamental mode of compulsory product certification for vehicles is:
Type Test + Initial Factory Inspection (enterprise quality assurance ability and product consistency inspection) + Post-certification surveillance
For mass-produced vehicle factories, the way of inspection of enterprise quality assurance ability and product consistency inspection of is the same as production consistency check.
For non-mass-produced vehicle enterprises, onsite sampling test/inspection and port sampling test or inspection should be also included besides quality assurance ability and product consistency inspection.
Post-certification surveillance can be follow-up inspection, onsite or port onsite sampling test/inspection and market sampling test/inspection independently or their combination.
5.
Determination of Certification Units
In principle, different automobiles are determined according to certification units. Certification applicant should submit the certification application to the certification body according to the rules of determination of certification units. Determination of series, units, type of certification automobiles refers to Appendix 2.
6.1 Submitting and Acceptance of Certification Application
Certification applicant should submit the certification application to the certification body in an appropriate way. Certification body should handle the application and respond to by a feedback of accepting or rejecting it within the time limit specified in implementation specifications.
Certification applicant should be responsible for product recall and three guarantees, including repair, change and return of product responsibilities.
The manufacturer and factory apply certification of products of automobiles and trailers which are in normal production. The certification body should not accept the application when it violates national laws and regulations and relevant industry policies.
6.2 Application Documents
Certification body should provide a list of application materials in its implementation specifications according to laws and regulations, standards and the needs of certification implementation, which should at least include the contents in Appendix 3.
Applicant should provide application documents as required in the implementation specifications. The certification body should review, manage and keep all relevant documents in confidence, and inform the applicant of the result.
6.3 Implementation Arrangement
Certification body and applicant should reach an agreement on the responsibility and arrangement of each party at every step of the certification implementation. According to the requirement of this Rules and implementation specifications and taking into consideration the actual situation and classification of the factory, the certification body should determine the specific certification implementation program and inform the applicant of it. The certification implementation program should at least include requirements for type test and initial factory inspection (when applied).
7 Certification Implementation
7.1.1Type Test Program
After document review, the certification body should develop a type test program and inform the applicant.
A type test program consists of all requirements and the quantity of samples, standard tested items and laboratory information.
Applicants can choose laboratory by themselves according to the scope determined by CNCA, but the development of program should consult the applicant.
7.1.2Requirements on Type Test Samples
In general, samples are selected and delivered to the laboratory by applicants according to the requirements for type test program. When necessary, according to the actual situation and classification of the factory, certification body could select samples onsite to obtain the sample and send it to the appointed laboratory.
The selection of samples according to the rules that whether the vehicles series tested program is the same type or not. Selecting only one sample if there are of the same type. Otherwise, selecting sample respectively. The quantity and requirements for sample should be determined by collecting all the sample. The quantity and requirements for sample refers to Appendix 4.
Applicant should guarantee the sample provided is consistent with manufactured products and can continuously produce. Certification body and/or laboratory should examine and verify the authenticity of the sample provided by the applicant. With any doubt of the authenticity, laboratory should explain to the certification body and deal with it in an appropriate way.
Certification body should specify in its implementation specifications the list of critical components and materials of products and relevant requirements and the conditions and detailed requirements of the accepted or acknowledged voluntary certification certificate or type test report according to relevant regulations announced by CNCA.
7.1.3 Type Test Program and Requirements
Based on the category and usage of vehicles chosen by applicants, certification bodies should determine Type Test Program according to this Rules. Test program and standards for test in this Rules refers to Appendix 1.
7.1.4 Implementation of Type Test
Type test should be conducted after certification body confirmed the application document summited by applicants in accordance with requirements for type test program. Certification body should consign the laboratory which is designated by CNCA to conduct the Type test.
The laboratory carries out type test on samples, records the entire process and archives the recordings in order to ensure the traceability of testing process and result.
If there is any failed test item, factory is allowed to rectify and send samples for re-test after the correction based on analyzing the reason resulting in failure. If the conclusion indicates that a re-test is needed, Laboratory should inform certification body of the test conclusion and certification body should determine a new test program.
For situations when approving test conclusion based on other conformity assessment system, certification body should specify the requirements in certification specification.
Note 2: Certification body and laboratory should add the requirements on sample check, video and photo recording, witness test, documentation, etc. for products with high safety risk, such as school bus, intercity bus, touring coaches, carrier for dangerous goods and refitted automobile. When necessary, relevant test items can be added.
Note 3: Criteria of Technology Determination for refitted automobile should be specified by certification body in certification specification and make an announcement to public.
If the factory meets the requirement of Implementation Rules for Compulsory Products Certification——Utilization of Testing Resources of Factory and Other Certification Results and requirement in certification standards, certification body can implement or witness type test by utilizing testing resources of factory. Designated laboratory should issue test report. Certification body should specify detailed requirements and procedure in the implementation specification.
7.1.5 Type Test Report
Certification body should determine a standardized format of type test report.
After type test, laboratories should provide the type test report to certification body and the applicant in a timely manner. The report should include the description of certification related information of the products within the application unit. The applicant should be able to provide complete and valid type test report to certification body and law enforcement parties during post-certification surveillance.
Initial factory review refers to the onsite review and evaluation for determining whether factory quality assurance ability, product consistency and standard conformity control meet the certification requirements or not.
In general, initial factory review should be performed after the type test. Upon request, the type test and initial factory review could be performed simultaneously.
7.2.1 Basic Principle
Certification applicant and factory should establish, implement and maintain systems of product consistency and standard conformity control according to Appendix 5 to ensure the certified products being consistent with certification requirements continuously.
Certification body should develop implementation specifications for factory review of automobile factories of mass-production and non-mass-production according to Implementation Rules for Compulsory Products Certification——Requirements for Factory Quality Assurance Ability and Implementation Rules for Compulsory Products Certification——General Requirements for Factory Inspection and implement consistency inspection of production consistency control system in factory to ensure factory review can be implemented. Inspection should cover product and processing premises of products applied for certification. When necessary, certification body should implement extended inspection outside the factory.
After the type test being satisfactory, initial factory inspection should be completed within 1 year in principle. Otherwise a new type test is needed.
7.2.2 Factory Review of Mass-Produced Vehicle
The implementation of factory review for mass-produced vehicle includes review on production consistency control plan and factory onsite review on production consistency.
7.2.2.1 Review on Production Consistency Control Plan
Manufacturer or factory of mass-produced vehicle should set up a production consistency control plan in accordance with Appendix 5 in this Rules and submit to certification body for review. Certification body should inform applicant of the review result.
If the production consistency control plan meets the requirements of review on production consistency specified in Appendix 5, the result of production consistency control plan is satisfactory. If certification body determines any flaws in the control plan, manufacturer or factory should correct it and re-sent the control plan. Certification body should conduct a new review of the plan and inform the certification applicant with the result.
If the certification body and manufacturer or factory fail to reach an agreement on production consistency control plan, with the precondition that the manufacturer or factory agrees and commits to cooperate with the certification body for the subsequent sampling and recheck, certification body can accept the production consistency control plan of manufacturer or factory.
After accepting the review on production consistency control plan of manufacturer or factory as satisfactory, certification body should design a production consistency inspection (factory onsite inspection) program, including products, premises and production consistency for inspection.
7.2.2.2 Factory Onsite Review on Production Consistency
If the review result of type test and production consistency control plan are satisfactory, certification body should designate an inspection team which consists of inspectors with registered national qualification to implement factory onsite inspection on production consistency.
During the inspection, products to be certified is in normal production in factory.
7.2.3 Factory Review of Non-Mass-Produced Vehicle
The implementation of factory review for non-mass-produced vehicle includes review on factory quality assurance ability and onsite check or inspection on production consistency.
For non-mass-produced vehicles that are refitted automobiles based on an uncertified automobile type (or certificate of automobile with basic type being suspension, withdrawal and cancellation), certification body should add the factory review on manufacturer or factory of basic automobile type combining the refitted items and contents.
7.2.3.1 Review on Factory Quality Assurance Ability and Production Conditions
Manufacturer or factory of non-mass-produced vehicle should, in accordance with requirements of Appendix 5 in this Rules, be equipped with related production and inspection condition, quality assurance ability and set up production consistency control measures to ensure the conditions for implementing factory review and onsite check or inspection of production consistency.
7.2.3.2 Onsite Sampling Test or Inspection of Production Consistency
Certification body should implement sampling test or inspection of product consistency on production onsite and warehouse, shipment premises confirmed during the review of factory quality assurance ability and production condition of non-mass-produced vehicle or after the review is being approved to be satisfactory.
7.2.5 Result of Factory Review
If non-conformity item is not found in the factory review, the review should be accepted as satisfactory.
In case of any non-conformity item found in factory review, it is allowed to make correction within a time limit (no longer than 3 months), and the certification body will verify the result of correction in an appropriate way. In case that the correction is overdue, or the correction results are unsatisfactory, the result of factory review will be unsatisfactory.
In case it is found in factory review that the implementation of the production consistency control plan deviate seriously with the one applied and approved, or any serious discrepancy is found on vehicle structure and technical parameters of vehicles produced and of the type test sample vehicle, the result should is found unsatisfactory, and the factory review will be terminated.
7.2.6 Timing of Factory Review
Timing of factory review is followed by certification according to related national regulations and should be specified in the implementation specification.
7.3 Evaluation and Determination of Certification
Certification body should make a comprehensive evaluation of the result of type test, initial factory inspection and relevant documents/information. A certificate will be issued according to units when evaluation is accepted as satisfactory. If the evaluation is unsatisfactory, the certification will be terminated.
7.4 Time Limit for Certification
Certification body should clarify on the time limit for each certification step and ensure certification being completed before the deadline. Applicant should actively cooperate in the certification process. In general, certificate should be issued to applicant within 90 days after the application being accepted.
8. Post-Certification Surveillance
Post-certification supervision refers to the surveillance activity carried out by certification body to monitor certificated products and its factory. Taking the classification and the actual situation of the factory into consideration, certification body should specify the requirements on the selection of the method of post-certification surveillance.
8.1.1 Principles of Follow-up Inspection
Certification body should implement effective follow-up inspection on certificated products and its factory based on factory classification with the aim of verifying the ongoing conformity of quality assurance ability of factories with certification requirements, and of ensuring the ongoing conformity of certificated products with standard requirements and products conformity with type test sample.
The follow-up inspection should be carried out during normal production of the manufacturer. For products manufactured discontinuously, certification applicant should provide relevant production schedule to the certification body to facilitate the effective implementation of follow-up inspection.
8.1.2 Content of Follow-up Inspection
Under the principle of ensuring certification risk is under controlled, certification body should determine the detailed requirements for follow-up inspection according to Appendix 5 and specify them in implementation specifications.
8.2 Onsite Sampling Test or Inspection
8.2.1 Principles of Onsite Sampling Test or Inspection
When onsite sampling test or inspection is adopted in post-certification surveillance, the certification applicant, manufacturers and enterprises should provide active cooperation.
8.2.2 Content of Onsite Sampling Test or Inspection
The certification body should specify the content and the requirement of onsite sampling test or inspection in implementation specifications according to the principle for factory classification and product characteristic. Certification body should develop the specific program for sampling test according to the content and requirement for onsite sampling and the designated person selects samples from qualified products (production line, storage and port). Sampling test could be implemented by utilizing testing resources of factory and the terms and conditions are the same as 7.1.4 in this Rules. For non-mass-produced vehicles, manufacturer should inform certification body before being sold/ exported based on conformity with requirements for factory onsite follow-up inspection. Certification body should develop specifications and carry out the structure & parameter inspection, and test of some non-destructive test project by way of randomly selecting 2 vehicles from 10 ones together with labs so as to ensure product consistency (less than 10 vehicles will be counted as 10 vehicles). When necessary, certification body should make sure that consistency inspection is implemented on each vehicle of each project. Certification bodies and laboratories determine whether some destructive test is needed or not according to the result of inspection and information for product quality every year.
Note 4: for school bus, intercity bus, touring coaches, trucks for dangerous goods, refitted vehicles and other products with high safety risk, the checking items should product check, photo or video records, documented information, when necessary, product consistency check and on-site sampling test should be included.
8.3 Market Sampling Test or Inspection
8.3.1 Principles of Market Sampling Test or Inspection
When market sampling test or inspection is adopted by post-certification surveillance, the certification applicant, manufacturer and enterprise should have cooperation and confirm the samples selected from the market.
8.3.2 Content of Market Sampling Test or Inspection
The certification body should specify the content and requirement for market sampling test or inspection in implementation specifications. Certification body develop sampling test program according to product characteristic and designate persons to select samples from certificated products on sale (including entire factory or users)
8.4 Application of Quality Information
The enterprises should build up system for collecting, summarizing, analyzing and saving customer complaints, and guarantee the transparency of complaint information to certification bodies without hiding or destroying relevant information. During follow-up inspection, the certification body should pay great attention to customer complaints, social focus, and investigation of defective products, risk prediction, huge quality accident, supervision & sampling test, special verification and quality information related to this Rule. Certification bodies should ensure that they only report to certification administration without leaking enterprise information to third parties. Certification bodies should establish system for collecting, summarizing, analyzing and saving customer complaints involving safety, environmental protection, energy saving and anti-theft so as to enhance the supervision on approved enterprises and products, meet the information need for government and improve the credibility of certification result. Certification body should meet general requirements provided by certification information.
8.5 Frequency and Timing of Post-Certification Surveillance
Certification body should implement post-certification surveillance at different frequencies among different types of factories and determine the timing of surveillance in a reasonable way basing on the factory classification. Specific principles should be specified in implementation specifications.
8.6 Recording of Post-Certification Surveillance
The certification body should record and archive the entire post-certification surveillance process to ensure the traceability of certification process and result.
8.7 Evaluation of the Results of Post-Certification Surveillance
The corrective action of the unsatisfactory item of the post-certification surveillance should be completed in 3 months. Otherwise, the test fails.
Certification bodies should make a comprehensive evaluation on the conclusion of follow-up inspections, sampling tests and relevant documents/information. The factory can keep using its certificate and certification mark after it passes evaluation; in case of a failure in the evaluation, the certification body should suspend or withdraw the certificate accordingly and make a public announcement.
8.8 Consistency Parameter Management
Certification bodies should have classified and dynamic parameter management of vehicle consistency, determine the potential safety quality risk of products according to change of parameter and so implement factory inspection and sampling if needed.
9.1 Maintenance of Certificate
The valid period of certificates is 5 years. Within valid period, the validity of the certificates are maintained through post- certification surveillance by certification bodies.
Certification consigner should submit a new certification application within 90 days before the expiration date of the certificate if he intends to extend the use of the certificate. If the result of the latest post-certification surveillance before expiration is found to be favorable, the certification body should directly renew the certificate.
Certificates should meet the requirement and content of Regulations for Compulsory Product Certification, and provide certificates with Appendixes indicating that the relevant product is consistent with the standards and the name and number of implementation rules for certification in this Rules. The change of certificate should note the version so as to highlight the frequency of change.
For multi-stage vehicles, previous manufactory and factories, vehicle types and unit information should be noted. If the product in previous stage which has been authorized with compulsory production certification should be identified with the number of certificate.
Certificates should specify that whether the product is a completed vehicle or not.
For products certified by non-mass-produced vehicle series, certificate should list vehicle identification number of covered product.
The components of integral vehicle, system and labelling information of assembly should be the same as the CCC certificate of components or the structural technical parameter that have been reported to certification bodies.
After authorized the certificate, if there are following changes--change of contents of the certificate, technical change of certificated products (design, structure parameter, key components/raw material, etc.) which affects the conformity of relevant standards, change of production consistency control plan or production conditions affecting production consistency, change of some items specified in certification implementation specifications, the applicant should submit an change application and implement change only after being approved by the certification body.
Certification body should specify in implementation specifications the detailed requirements for change of certificate, including the scope and procedure of change. Certification bodies should evaluate provided documents according to contents of change and so decide whether approve the change. Certification bodies can approve the change only after the result of the test and/or inspection is satisfactory when the sampling test and/or factory inspection is needed. Sampling test can utilize testing resources of factories and the terms and requirements are the same as Terms of 7.1.4.
Change can be approved if it is consistent with requirement. The number and valid period for the new certificates are the same as the old ones and the approved date of change should be noted. If there is no need for new certificates, provide changed conformation table, and note the new content and the approved date of change.
9.4 Suspension, Cancellation, and Withdrawal of the Certificate
Suspension, cancellation and withdrawal of the certificate should follow Regulations for Compulsory Product Certification, Implementation Rules for Cancellation, Suspension and Withdrawal of Compulsory Product Certification and relevant regulations of certification implementation specifications.
Certification bodies should establish risk prediction mechanism for certificated products. Certification bodies can suspend and withdraw the certificate when there are big design defect or potential safety hazard (such as safety alarming, defect inspection, recall of products, big quality accident or much nonconformity found in supervision inspection and special verification) and manufacturers should responsible for it after being verified.
The certification body should determine the categories and range of products which do not conform to certification requirements and make an announcement of the certificates being cancelled, suspended or withdrawn in an appropriate manner.
Certification body should make sure that the usage of certificates comply with Regulations for Compulsory Product Certification.
10. Certification Mark and Certificate for Vehicle Consistency
The management and usage of the certification mark should follow Regulations for Compulsory Product Certification Mark.
The certificated products of vehicles and trailers adopt the certification mark “S”. The design of the mark is as follows:

The vehicles granted with CCC certificates should be attached with CCC marks as required on the top right of frontal windscreen (in running direction) and the marks on trailers should be attached at visible position. The mark size should be 60mm. The multi-stage built vehicles approved at stages should keep marks for each stage.
10.3 Certificate for Product Consistency
Manufactures or factories should submit parameter and sample of certificate for vehicle consistency to certification bodies according to the Implementation Rules. The content of mode, relevant requirements and parameter of product consistency refer to Appendix 6. Documents of each certificated vehicle should be enveloped with certificate for product consistency so as to present the information of certificated products, environmental protection and fuel consumption indices to consumers or relevant departments.
The certification should be charged by certification body and laboratory according to national regulations on fees and charges for compulsory products certification.
The certification body should reasonably determine the specific fees and charges per day per person of initial factory inspection and re-check of post-certification surveillance of compulsory product certification according to the national regulations on fees and charges.
12. Certification Responsibility
The certification body should be responsible for its certification conclusions.
The laboratory should be responsible for its testing results and reports.
The certification body and factory inspector assigned by it should be responsible for factory inspection conclusion.
The certification applicant should be responsible for the authenticity and lawfulness of the documents and samples submitted for certification.
13. Implementation Specifications
The certification body should, according to the principles and requirements of this Rules, develop scientific, reasonable and practical implementation specifications for certification. The implementation specifications should be announced to the public after being submitted to CNCA for records. Implementation specifications should at least include the following aspects:
(1)Certification procedure and requirements of time limit;
(2)Selection of certification mode and relevant requirements;
(3)Requirements on factory’s classification management;
(4)Application documents for certification and relevant requirements;
(5)Requirements on sample testing (including requirements for onsite/market sampling test or inspection);
(6)Requirements on initial factory inspection
(7)Requirements for post-certification surveillance
(8)Requirements for utilizing testing resources of factory and Utilization of other result of certification
(9)Requirements for change of certificate (including change of standard)
(10)Requirements and List of critical components and materials;
(11)Reference for fees and charges and relevant requirements;
(12)Requirements on the procedures and time limit related to technical disputes and complaints.
Appendix 1: Type Test Items and Criteria
01 General Safety
�-01
Marks
Marks of motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirement of GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power driven vehicles operating on roads” and GB 30509 “ Identification for passenger cars and their parts”; Besides, gas fuel vehicles dual-purpose vehicles and two fuel vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 17676 “gas vehicle and liquefied petroleum gas vehicle Identification marks”; marks of dangerous goods carrying vehicles on the road shall comply with the requirement in GB 13392 “Marks of Road Dangerous Goods Carrying Vehicles”(dangerous goods refer to GB12268 “List of dangerous goods”).School bus mark shall comply with the requirement of GB 24315 "The marker for school bus".
�-02
VIN
Motor vehicles and trailers must have VIN and VIN shall comply with the requirement of GB 16735 “Road Vehicles Vehicle’s Identification Number (VIN)”.
�-03
Dimension, Axle Load and Mass
01-03-01 Overall Dimension, Axle Load and Mass
Overall dimension, axle load and mass of motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirement of GB 1589 “Limit Value of Road Vehicles’ Overall Dimension, Axle Load and Mass”.
01-03-02 Rear Suspension
Rear suspension of motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirement of GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power driven vehicles operating on roads”.
01-03-03 Load Capacity Ratification
The load capacity of motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power driven vehicles operating on roads”.
01-03-04 Specific Power
The specific power of motor vehicle shall comply with GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power driven vehicles operating on roads”.
�-04
Side-Tipping Stabilizing Angle
The test of side-tipping stabilizing angle of motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 14172 “Static roll stability test method for motor vehicles”. The result shall comply with the requirement of GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power driven vehicles operating on roads” and GB 28373-2012 “Tank vehicles of categories N and O with regard to rollover stability”.
�-05
Forward Visibility for Drivers
Drivers’ forward visibility of Category M1 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 11562 “Motor vehicles-Forward visibility for drivers-Requirements and measurement methods”.
�-06
Devices for Indirect Vision
The performance of motor vehicle mirrors and the installation of indirect vision devices shall comply with the requirements of GB 15084 “Motor vehicles - Devices for indirect vision - Requirements of performance and installation”.
�-07
Windscreen Defrosting Device
Defrosting device of Category M1 vehicles’ windscreen shall comply with the requirement of GB 11555 “Motor vehicles-windshield demisting and defrosting systems - Performance requirements and test methods”. Among them, defrosting device of electric vehicles’ windscreen shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 24552 “Electric vehicles - Windshield demisters and defrosters system - Performance requirements and test methods”.
�-08
Windscreen Demisting Device
Demisting device of Category M1 vehicles’ windscreen shall comply with the requirement of GB 11555 “Performance Requirement and Testing Methods of Demisting System of Vehicles’ Windscreen”. Among them, demisting device of electric vehicles’ windscreen shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 24552 “Electric vehicles - Windshield demisters and defrosters system - Performance requirements and test methods”.
�-09
Wiper of Windscreen
All kinds of vehicles shall be equipped with windscreen wiper, among them, Category M1 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 15085 “Performance Requirement and Testing Methods of Wiper, Washer of Vehicle Windscreen”.
�-10
Washer of Windscreen
All kinds of motor vehicles shall be equipped with windscreen washer, among them, Category M1 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 15085 “Performance and Testing Methods of Wiper, Washer of Motor Vehicle Windscreen”.
�-11
Speedometer
Motor vehicle’s speedometer shall comply with the requirement of GB 15082 “Speedometer for Motor vehicles”.
�-12
Horn
The performance and the Installation of horn shall comply with the requirements of GB 15742 “Performance requirements and test methods of horn for motor vehicles”.
�-13
Graphic Mark of Manipulation Units, Indicator and Signal Device
All the graphic marks manipulation units, indicators and signal devices in the motor vehicle shall comply with the requirement of GB 4094 “Symbols of Motor Vehicle’s Manipulation Units, Indicators and Signal Devices”. Among them, electric vehicle shall comply with the requirements of GB/T 4094.2 “Electric vehicles—Symbols for controls, indicators and tell-tales”.
�-14
License Plate
License plate of motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirement of GB 15741 “The license plates (crackets) and its position on motor vehicles and trailer” and GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power-driven vehicles operating on roads”.
�-15
Fuel System and Exhaust Pipe
Fuel system (including gas fuel) and exhaust pipe of the motor vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 7258”Safety specifications for power driven vehicles operating on roads”.
�-16
Hood Latch System
The hood latch system of motor vehicle shall comply with the requirements of GB 11568 “Motor vehicles-hood latch system”.
�-17
Protective Devices Against Unauthorized Use
The protective devices of motor vehicle shall comply with the requirements of GB15740“Protective devices against unauthorized use of motor vehicles”.
�-18
Travelling Data Devices
All school buses, highway coach and touring coach, buses without passengers standing area, dangerous goods carrying vehicles, tractor and truck with gross mass more than or equal to 12,000 kg shall be equipped with travelling data devices (GPS devices with the travelling data recording function is considered as the travelling data devices) that can record, store up, show and print information on the vehicle’s running speed, time and road haul. The travelling data devices shall comply with the requirements of GB/T 19056 “Vehicle travelling data recorder”.
�-19
Bus Structure
Structure of Class I, II and III single deck buses in Category M2 and M3 Vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 13094 “The safety requirements for bus construction”. Structure of Class A and B single deck buses in Category M2 and M3 Vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 18986 “The Safety Requirements for Light bus construction”. The sleeper bus shall comply with the requirements of GB/T 16887 “Safety requirements for sleeper bus construction”. The double-deck large passenger vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB/T19950 “The safety constructional requirements for double-deck large passenger vehicles”. The special school buses shall comply with the requirements of GB 24407 “The safety technique specifications of special school buses”. In addition, all buses shall comply with the requirements of GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power-driven vehicles operating on roads”.
�-20
Safety Specifications for Road Transportation Vehicle of Explosive Substance and Chemical Toxic Substance
The road transportation vehicle of explosive substance and chemical toxic substance shall comply with the requirements of GB 20300 “Safety specifications for road transportation vehicle of explosive substance and chemical toxic substance”.
�-21
Provisions of Vehicles for the Carriage of Dangerous Goods With Regard to Their Specific Constructional Features
The vehicles for the carriage of dangerous goods shall comply with the requirements of GB 21668 “Provisions of vehicles for the carriage of dangerous goods with regard to their specific constructional features”.
�-22
Safety Requirement for Power-Driven Vehicles Operation
Function of overspend alarm and limit speed, seats arrangement and orientation, Truck safety box shall comply with the requirements of GB 7258“Safety specifications for power-driven vehicles operating on roads”.
02 Passive Safety
02-01 Door Lock
Category M1 and N1 vehicles’ door locks shall comply with the requirements of GB 15086 “Motor vehicles—Door locks and door retention components—Performance requirements and test methods”.
02-02 Door Retention Components
The door retention components (Door hinges/sliding door system) in Category M1 and N1 Vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 15086 “Motor vehicles—Door locks and door retention components—Performance requirements and test methods”.
02-03 Seats and Fixtures
The seats and fixtures in category M1 and N vehicles, seats and fixtures intended for Class A and I passenger vehicles in Category M2 and M3 vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 15083 “Strength requirement and test of motor vehicle seats, their anchorages and any head restraints”. Seats and fixtures intended for passenger vehicles except Class A and I in Category M2 and M3 vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 13057 “Strength of the seats and their anchorages of passenger vehicles”. The seats and fixtures for special school bus shall comply with the requirements of GB 24406 “The strength of student seat systems and their anchorages of special school bus”.
02-04 Passengers Protection from Luggage Displacement
The seat or isolation device of luggage compartment in category M1 vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 15083 “Strength requirement and test of motor vehicle seats, their anchorages and any head restraints”.
02-05 Motor Vehicle Seats Head Restraints
The seats head restraints of motor vehicle shall comply with the requirements of GB 11550 “Strength requirement and test of motor vehicle seats head restraints”.
02-06 Safety Belt and Children Restrain System
All seats of passenger car, road passenger vehicle, touring coach, bus without passenger standing area, special school bus and trailer caravan, driver seats and front passenger seats of other motor vehicles (excluding low-speed vehicle) shall be equipped with safety belts. Among them, all driver seats and front passenger seats (excluding the middle seats of the passenger seats in front rows of trunk and bus with passenger standing area), crew member seats in the stepping area of passenger vehicle and all seats of passenger car except middle seats at second row and behind shall be equipped with three-point(four point) style safety belt; each student seat(chair) of special school buses and non-special school buses but dedicated to transfer to and from school and sleeper of sleeper coach shall be equipped with two-point style safety belt. Performance of the safety belt shall comply with the requirements of GB 14166 “Safety-belts, restraint systems, child restraint systems and ISOFIX child restraint systems for occupants of power-driven vehicles”; the installation of safety belt and children restrain system in vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 14166 “Safety-belts, restraint systems, child restraint systems and ISOFIX child restraint systems for occupants of power-driven vehicles”.
02-07 Safety-Belt Anchorages, ISOFIX Anchorages
Safety-belt anchorages of all seats of passenger car, road passenger vehicle, touring coach, bus without passenger standing area, special school bus and trailer caravan, driver seats and front passenger seats of other motor vehicles (excluding low-speed vehicle) shall comply with the requirements of GB 14167 “Safety-belt anchorages, ISOFIX anchorages systems and ISOFIX top tether anchorages for vehicles”.
At least one seat of passenger car (excluding single-roll car) shall equipped with ISOFIX children seat anchorages devices that meets the standard requirements, or at least one seat in back roll is functioned to enable the anchoring of children seat by using safety belt. Anchorages devices shall comply with the requirements of GB 14167 “Safety-belt anchorages, ISOFIX anchorages systems and ISOFIX top tether anchorages for vehicles”.
02-08 External Projections
The external projections of category M1 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 11566 “External projections for passenger car”; the external projections of cab of category N vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 20182 “The cab of commercial vehicles—External projections”.
02-09 Interior Fittings of Passenger Car
The internal projections of Category M1 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 11552 “The interior fittings of passenger car”.
02-10 Wheel Guards
The wheel guards of Category M1 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 7063 “The wheel guards of motor vehicles”.
02-11 Roof Crush Resistance of Passenger Cars
The roof crush resistance of Category M1 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 26134 “Roof crush resistance of passenger cars”.
02-12 Front and Rear Protective Devices
The front and rear protective devices of Category M1 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 17354“Front and rear protective devices for passenger cars”.
02-13 Stipulation Protecting Drivers from Being Injured By Motor Vehicle Steering Mechanism
The stipulation protecting drivers from being injured by motor vehicle steering mechanism of category M1 vehicles and category N1 vehicles whose gross mass is less or equal to 1500kg shall comply with the requirement of GB 11557 “The stipulation protecting drivers from being injured by motor vehicle steering mechanism”.
02-14 Protection of the Occupants in the Event of a Frontal Collision
The protection of the occupants in the event of a frontal collision of category M1 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 11551“The protection of the occupants in the event of a frontal collision for passenger car”.
02-15 Protection of the Occupants in the Event of a Lateral Collision
The protection of the occupants in the event of a lateral collision of category M1 and N1 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 20071“The protection of the occupants in the event of a lateral collision”.
02-16 Requirements of Fuel System Safety in the Event of Rear-End Collision
The requirements of fuel system safety in the event of rear-end collision of category M1 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 20072 “The requirements of fuel system safety in the event of rear-end collision for passenger car”.
02-17 Strength for the Superstructure of Bus
The strength for the superstructure of bus of Class B, I and II passenger vehicle and special school bus in category M2 and M3 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 17578 “Requirements and test methods of strength for the superstructure of bus”.
02-18 Protection of the Occupants of the Cab of a Commercial Vehicle
The protection of the occupants of the cab of category N vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 26512 “The protection of the occupants of the cab of a commercial vehicle”.
02-19 Front Underrun Protection for Commercial Vehicle
The front underrun protection of category N2 and N3 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 26511 “Front underrun protective requirements for commercial vehicle”.
02-20 Motor Vehicles and Trailers--Lateral Protection
The motor vehicles and trailers--Lateral protection of category N2,N3,O3 and O4 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 11567.1 “Motor vehicles and trailers--Lateral protection requirements”.
02-21 Motor Vehicles and Trailers--Rear Underrun Protection
The motor vehicles and trailers--Rear underrun protection of category N2,N3,O3 and O4 vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 11567.2 “Motor vehicles and trailers--Rear underrun protection requirements”.
02-22 Windscreen
The windscreen of motor vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 9656“Safety glazing materials for road vehicles”.
02-23 Flammability of Interior Materials
The flammability of automotive interior materials shall comply with the requirement of GB 8410“Flammability of automotive interior materials”.
02-24 Fuel Tank
The automobile fuel tank shall comply with the requirement of GB 18296“Safety property requirements and test methods for automobile fuel tank”.
02-25 Unique Items for Electric Vehicles
The safety specification of electric vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 18384.1 “Electric vehicles--Safety specification--Part 1: On-board energy storage”, GB/T 18384.2 “Electric vehicles--Safety specification--Part 2: Functional safety means and protection against failures”, GB/T 18384.3 “Electric vehicles--Safety specification--Part 3: Protection of persons against electric hazards”; magnetic and electric field strength shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 18387 “Limits and test method of magnetic and electric field strength from electric vehicles,broadband,9kHz to 30MHz” ; electric vehicles accumulator shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 18332.1 “Lead-acid batteries used for electric road vehicles”, QC/T 743 “Lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles”, QC/T 744 “Nickel-metal hydride batteries for electric vehicles”, GB/Z 18333.2 “Zinc-air batteries for electric road vehicles”; conductive charging system shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 18487.1 “Electric vehicle conductive charging system--Part 1: General requirements”.
02-26 Unique Items for Hybrid ElectricVehicles
The safety specification of Hybrid electric vehicles shall comply with requirement of GB/T 19751 “Hybrid electric vehicles safety specification”; magnetic and electric field strength shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 18387 “Limits and test method of magnetic and electric field strength from electric vehicles,broadband,9kHz to 30MHz” ; electric vehicles accumulator shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 18332.1 “Lead-acid batteries used for electric road vehicles”, QC/T 743 “Lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles”, QC/T 744 “Nickel-metal hydride batteries for electric vehicles”, GB/Z 18333.2 “Zinc-air batteries for electric road vehicles”; conductive charging system shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 18487.1 “Electric vehicle conductive charging system--Part 1: General requirements”.
02-27 Unique Items for Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles
The safety specification of Fuel cell electric vehicles shall comply with requirement of GB/T 24549 “Fuel cell electric vehicles - Safety requirements”; magnetic and electric field strength shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 18387 “Limits and test method of magnetic and electric field strength from electric vehicles,broadband,9kHz to 30MHz”.
03 Environment Protection and Energy Saving
03-01 Exhaust of Motor Vehicles With GVM ≤ 3,500kg
The exhaust of motor vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 18352.3 “Limits and measurement methods for emissions from light-duty vehicles” or GB 18352.5 “Limits and measurement methods for emissions from light-duty vehicles (CHINA 5)”,among them, the test of hybrid electric vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 19755 “Measurement methods for emissions from light-duty hybrid electric vehicles” or GB 18352.5 “Limits and measurement methods for emissions from light-duty vehicles (CHINA 5)”; exhaust smoke of free acceleration from vehicles equipped with compression ignition engine shall comply with the requirement of GB 3847 “Limits and measurement methods for exhaust smoke from C.I.E(Compression Ignition Engine) and vehicle equipped with C.I.E.”
03-02 Emission of Motor Vehicles with GVM > 3,500kg
03-02-01 Ignition Engine Motor Vehicles
Exhaust pollutant of engines shall comply with the requirement of GB 14762 “Limits and measurement method for exhaust pollutants from positive ignition (P.I.) engines of vehicles and vehicles equipped with P.I. engines”; two-speed idle pollutants of motor vehicle shall comply with the requirement of GB 18285 “Limits and measurement methods for exhaust pollutants from vehicles equipped ignition engine under two-speed idle conditions and simple driving mode conditions”; Motor vehicle’s crankcase pollutants shall comply with the requirement of GB 11340 “Limit and measurement methods for crankcase pollutants From heavy-duty vehicles equipped with P.I engines”; Motor vehicle’s evaporation pollutants shall comply with the requirement of GB 14763 “Limit and measurement methods for fuel evaporative Pollutants from heavy-duty vehicles equipped with P.I engines (Trap method)”; Durability of Emission Control Systems shall comply with the requirement of GB 20890 “Test Procedures and Requirement of Durability of Emission Control Systems for Heavy-duty Vehicles”.
03-02-02 Compression-Ignition Engine Motor Vehicles
Exhaust pollutant of engines shall comply with the requirement of GB 17691 “Limits and measurement methods for exhaust pollutants from compression ignition and gas fuelled positive ignition engines of vehicles(Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ)”;Exhaust smoke from engine shall comply with the requirement of GB 3847 “Limits and measurement methods for exhaust smoke from C.I.E(Compression Ignition Engine) and vehicle equipped with C.I.E.”; Durability of Emission Control Systems shall comply with the requirement of GB 20890-2007 “Test Procedures and Requirement of Durability of Emission Control Systems for Heavy-duty Vehicles”.
03-03 Net Power for Automotive Engines
The net power for automotive engines(indicated value)shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 17692 “Measurement methods of net power for automotive engines”.
03-04 Refrigerant of Air-Conditioner
Air-conditioners in the motor vehicles shall use mark or relevant certificating documents of refrigerants, CFC12 is forbidden.
03-05 Radio Disturbance Characteristics
The Radio disturbance characteristics of motor vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 14023 “Vehicles, boats and internal combustion engine - Radio disturbance characteristics - Limits and methods of measurement for the protection of off-board receivers”.
03-06 Fuel Consumption
03-06-01 Passenger Car
The evaluation of fuel consumption limit for passenger car shall comply with the requirement of GB 27999 “Fuel consumption evaluation methods and targets for passenger cars” by designated organizations according to the average fuel consumption of enterprises mix,and the test shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 19233“Measurement method of fuel consumption for light-duty vehicle”. Among them, the test of Hybrid electric vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 19753 “Test methods for energy consumption of light-duty hybrid electric vehicles”. Fuel consumption label for passenger car shall comply with the requirement of GB 22757 “Fuel consumption label for light vehicle”.
03-06-02 Light Duty Commercial Vehicles
The fuel consumption for light duty commercial vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 20997 “Limits of fuel consumption for light duty commercial vehicles”,and the test shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 19233“Measurement method of fuel consumption for light-duty vehicle”. Among them, the test of Hybrid electric vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 19753 “Test methods for energy consumption of light-duty hybrid electric vehicles”. Fuel consumption label for passenger car shall comply with the requirement of GB 22757 “Fuel consumption label for light vehicle”.
03-06-03 Heavy Duty Commercial Vehicles
The fuel consumption for heavy duty commercial vehicles shall comply with the requirement of GB 30510 “Fuel consumption limits for heavy-duty commercial vehicles”,and the test shall comply with the requirement of GB 27840“Fuel consumption test methods for heavy-duty commercial vehicles”.
03-07 Recyclability and Recoverability of Motor Vehicles and Trailers
The recyclability and recoverability of motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 19515 “Road vehicles—Recyclability and recoverability—Calculation method”.
03-08 Prohibited Substances
The prohibited substances of motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirement of GB/T 30512 “Requirements for prohibited substances on automobiles”.
04 External Lighting and Light Signaling Device
04-01 Installation of the External Lighting and Light-Signaling Devices
The installation of the external lighting and light-signaling devices for motor vehicles and their trailers shall comply with the requirement of GB 4785 “Prescription for installation of the external lighting and light-signaling devices for motor vehicles and their trailers”.
04-02 Headlamp Beam Exposure Location and Luminous Intensity
The motor vehicle headlamp beam exposure location and luminous intensity shall comply with the requirement of GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power-driven vehicles operating on roads”.
04-03 Front Light Distribution Performance
The front light distribution performance of motor vehicle shall comply with the requirement of GB 4599 “Motor vehicle headlamps equipped with filament lamps”, GB 21259 “Headlamps equipped with gas-discharge light sources for motor vehicle”, GB 25991 “Automotive headlamps with LED light sources and/or LED modules”, GB/T 30036 “Adaptive front-lighting system for motor vehicles”.
04-04 Direction Indicators
Photometric characteristics of direction indicators for motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirements of GB 17509 “Photometric characteristics of direction indicators for motor vehicles and trailers”.
04-05 Position Lamps
Photometric characteristics of position lamps for motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirements of GB 5920 “Photometric characteristics of front and rear position lamps, end-outline marker lamps and stop lamps for motor vehicles and trailers”.
04-06 End-Outline Marker Lamps
Photometric characteristics of end-outline marker lamps for motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirements of GB 5920 “Photometric characteristics of front and rear position lamps, end-outline marker lamps and stop lamps for motor vehicles and trailers”.
04-07 Stop Lamps
Photometric characteristics of stop lamps for motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirements of GB 5920 “Photometric characteristics of front and rear position lamps, end-outline marker lamps and stop lamps for motor vehicles and trailers”.
04-08 Reversing Lamps
Photometric characteristics of reversing lamps for power-driven vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 15235 “Photometric characteristics of reversing lamps for power-driven vehicles”.
04-09 Front Fog Lamps
Photometric characteristics of front fog lamps for motor vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 4660 “Motor vehicle front fog lamps equipped with filament lamps”.
04-10 Rear Fog Lamp
Photometric characteristics of rear fog lamp for power-driven vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirements of GB 11554 “Photometric characteristics of rear fog lamp for power-driven vehicles and trailers”.
04-11 Side-Marker Lamps
Photometric characteristics of side-marker lamps for motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirements of GB 18099 “Photometric characteristics of side-marker lamps for motor vehicles and trailers”.
04-12 Rear Registration Plate Lamp
Photometric characteristics of rear registration plate lamp for motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirements of GB 18408 “Photometric characteristics of devices for the illumination of rear registration plates of motor vehicles and trailers”.
04-13 Parking Lamps
Photometric characteristics of parking lamps for motor vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 18409 “Photometric characteristics of parking lamps for power-driven vehicles”.
04-14 Daytime Running Lamps
Photometric characteristics of daytime running lamps for motor vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 23255 “Photometric characteristics of daytime running lamps for motor vehicles”.
04-15 Cornering Lamps
Photometric characteristics of cornering lamps for motor vehicle shall comply with the requirements of GB/T 30511 “Photometric characteristics of cornering lamps for motor vehicle”.
04-16 Retro Reflector
Photometric characteristics of retro reflector for motor vehicle and trailers shall comply with the requirements of GB 11564 “Retro reflector for motor vehicles”.
04-17 Retro-Reflective Markings
Truck, including the semi-trailer tractor, refitted truck chassis of special motor vehicle and trailer with the exception of setting up in conformity with the provisions tail sign board, shall be set retro-reflective markings in back; truck, including the semi-trailer tractor, refitted truck chassis of special motor vehicle and trailer shall set retro-reflective markings on the side, retro-reflective markings shall comply with the requirements of GB 23254 “Retro-reflective markings for trucks and trailers”, GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power-driven vehicles operating on roads”.
04-18 Rear-Marking Plates for Vehicles and Trailers
Truck with its gross mass greater than or equal to 12,000 kg ( excluding the semi-trailer tractor), special motor vehicle refitted by truck chassis and trailer with its length more than 8 meters shall be set rear-marking plates, rear-marking plates shall comply with the requirements of GB 25990 “Rear-marking plates for vehicles and trailers”.
04-19 Headlamp Cleaner
Headlamp cleaner of motor vehicle shall comply with the requirements of GB 21260 “Headlamp cleaner”.
05 Noise and Chassis
05-01 Noise Emitted By Accelerating Motor Vehicles
Noise emitted by accelerating motor vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 1495 “Limits and measurement methods for noise emitted by accelerating motor vehicles”.
05-02 Noise Emitted By Stationary
The test of noise emitted by stationary motor vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB/T 14365 “Acoustics-Measurement of noise emitted by stationary road vehicles”.
05-03 Steering Equipment
Steering equipment of motor vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 17675 “Steering system of motor vehicles-Basic requirements”.
05-04 Braking Systems
05-04-01 Structure and Performance
Structure and performance of braking systems of category M1 vehicle shall comply with the requirements of GB 21670 “Technical requirements and testing methods for passenger car braking systems”; structure and performance of braking systems of other motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirements of GB 12676 “Road vehicle--Braking systems--Structure, performance and test methods”.
05-04-02 Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) Performance
The highway coach and touring coach, buses without passengers standing area with length over 9 meters, all special school buses, dangerous goods carrying vehicles and semi- trailer tractor, special working truck and truck with gross mass more than or equal to 12,000 kg and trailer with gross mass more than 10,000 kg shall be equipped with ABS. ABS performance of M1 category motor vehicle shall comply with the requirements of GB 21670 “Technical requirements and testing methods for passenger car braking systems”; ABS performance of other motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirements of GB/T 13594 “Antilock braking performance and test procedure for motor vehicles and trailers”.
05-05 Brake Hose
Brake hose of motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirements of GB 16897 “Brake hose - Structure, performance and test methods”.
05-06 Tyres
Tyres of passenger cars shall comply with the requirements of GB 9743 “Passenger car tyres”; Tyres of other motor vehicles and trailers shall comply with the requirements of GB 9744 “Truck tyres”.
06 Special Devices and Functions of Special Purpose Vehicles
06-01 Mass Parameters
Mass parameters of special device shall comply with the requirements of GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power-driven vehicles operating on roads”; the rated towed mass of the wrecker vehicle shall not exceed its maximum gross mass.
06-02 On-Board Electric System
Truck crane, all terrain crane shall comply with the requirements of JB 8716 “Truck crane and wheel crane --Safety code”; aerial working truck shall comply with the requirements of JG 5099 “Safety rules for aerial work machinery”; electric systems in the concrete pump vehicle shall be equipped with emergency stop switches and grounding devices. Insulation resistance shall be no less than 0.5MΩ. Electrical control system shall have the control function of pumping, reversing pumping, stop pumping and other functions. The electric system shall have overload protective device to ensure the safety.
06-03 Dangerous Signs
Tankers for carrying hazardous chemicals shall be equipped with notice at the rear of vehicles or tanks. The name, type, attribute, available capacity, the loaded mass, first-aid measures, enterprise contact number and words of “poison” and “explosive” sprayed on both sides and rear of the vehicles; the signs of vehicles for carrying hazard shall comply with the requirements of GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power-driven vehicles operating on roads”; the signs of crane lifting types of vehicles shall comply with the requirements of GB 15052 “Lifting appliances--Dangerous positions and signs”. The signs of flexible leg and other danger location in the concrete pump vehicle shall comply with the requirements of GB 15052 “Lifting appliances--Dangerous positions and signs”.
06-04 Container and Pipeline
The total capacity limit of the tanker loading matters other than not those mentioned in the GB 12268 “List of dangerous goods” shall meet the following formula:
Total volume (m3) ≤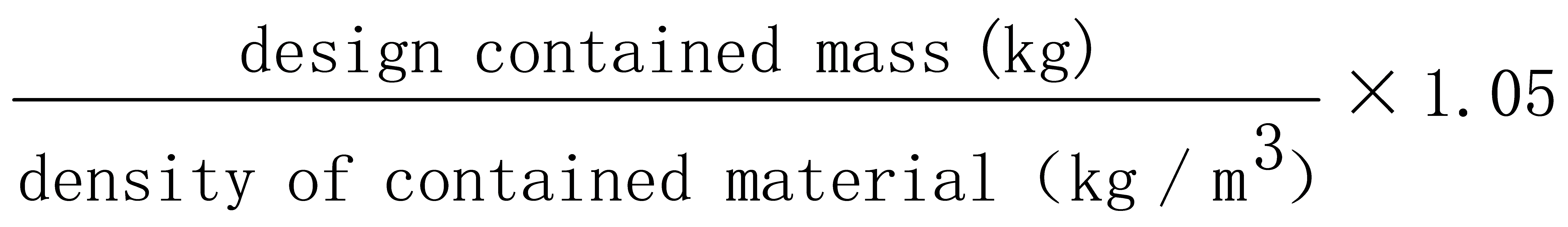
The total capacity limit of the tanker loading matters mentioned in the GB 12268 “List of dangerous goods” shall meet the following formula:
Total volume “m3”≤ 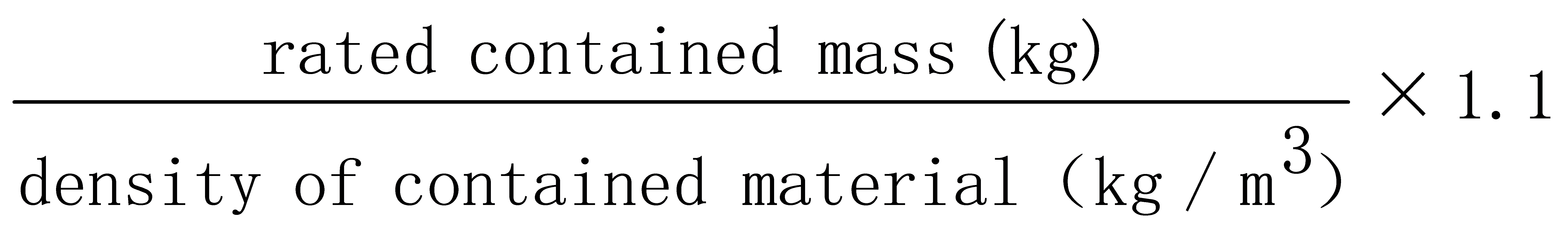
The valid capacity of tanker for explosive products transport should be no more than 20 m3.
The valid capacity of tanker for hazardous chemicals transport should be no more than 10 m3.
The oil tank of the oil tanker shall be able to withstand at least 35kPa air pressure. No leakage and permanent deformation are allowed; Inlet line shall be leakage free in self-absorption tests; pressure piping shall have no leakage in operation.
06-05 Electrostatic Conductivity Device
Special purpose vehicles for transporting inflammable substance shall comply with the requirements of GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power-driven vehicles operating on roads”; the size, balance weight mass, tensile strength, hardness and electrostatic conductivity of the drag stripe shall comply with the requirements of JT 230 “Rubber belt of electrostatic conductivity for motor vehicle”.
06-06 Fire Service Check
Special purpose vehicles for transporting inflammable and explosive substance and special purpose vehicles having special requirements for operating environment shall meet the requirements of GB 7258 “Safety specifications for power-driven vehicles operating on roads”.
06-07 Operation Noise
When tankers work under rated flow, the noise at a distance of 1.0 m in front of the middle of the operating cab and height of 1.5 m above the ground shall comply with: The chassis engine power: noise ≤90dB(A); self-contained engine: ≤94dB(A); the operating noises of the crane truck and the truck with loading crane shall comply with the requirements of GB 20062 “Mobile crawler crane--Limits and measurement methods for operating noise”; operation noise of concrete truck mixer shall comply with the requirements of GB/T 26408 “Concrete truck mixer”; operation noise of concrete pump truck shall comply with the requirements of QC/T 718 “Concrete pump truck”.
06-08 Safety Protection Devices
Truck crane, all terrain crane shall comply with the requirements of JB 8716 “Truck crane and wheel crane --Safety code”; torque limiter shall comply with the requirements of GB 12602 “Lifting appliances-safety devices against overloading”; Aerial working vehicle shall comply with the requirements of JG 5099 “Safety rules for aerial work machinery”; and the lifting vehicles shall be equipped with amplitude indicator with specific figures. The accuracy of the indicator: When the amplitude is less than or equal to 5 m, the deviation shall be no more than 100mm, and when the amplitude is greater than 5m, the deviation shall be no more than 2% of the amplitude. Electric systems shall have safety guard. Every oil tank shall be fitted with locking apparatus to prevent self-stretching of the cylinder rod of the tank. Lifting hook of folding arm truck with loading crane shall be equipped with devices to prevent wire rope from pulling out; concrete pump vehicle shall be equipped with the level meter, proper measures shall be taken for the cloth to prevent a sudden fall of the front hose of the carrier pipe. As for the self-dumping truck and dumping garbage trucks, bar stay preventing a fall of the carriage or other reliable emergency apparatus shall be installed under the carriage; the sewage absorbing vehicle using vacuum pump as a source of absorbing system shall have a decontamination device.
06-09 Operating System
Truck crane, all terrain crane shall comply with the requirements of JB 8716 “Truck crane and wheel crane --Safety code”; Aerial working vehicle shall comply with the requirements of JG 5099 “Safety rules for aerial work machinery”; the mixing tube of the concrete mixing carrier vehicle shall be equipped with a light and flexible speed control lever with locking devices and the lever control marks indicating the direction and position while feeding, stirring and discharging; compression garbage trucks shall have button or hand lever for movement stopping and counter-movement on the side of loading and unloading device, and eye-catching marks shall be placed.
06-10 Vehicle Stability
Truck crane, all terrain crane shall comply with the requirements of JB 8716 “Truck crane and wheel crane --Safety code”; Aerial working vehicle shall comply with the requirements of JG 5099 “Safety rules for aerial work machinery”; the static stability burdening value of the obstacle removing truck with rotary boom and truck with loading crane shall be not less than 1.25PQ + 0.1F (PQ- maximum lifting mass F is converted to the load produced by the mass of main arm support and small arm of head of the arm support or the head of little arm). The overload protection device installed on the vehicle shall not have any artificial device failure. The static stability burdening value shall be ultimate load to enable lifting under the operating mode. The concrete pump vehicle shall meet the following requirements: under the 1.25 times the work load with the distribution shift at the most disadvantaged position relative to vehicle stability, at least three of the landing legs shall not loose; regardless of the position of distribution shift, one of the landing legs can be allowed to rise, but the travel of leg rising shall not exceed 200mm; longitudinal stability of the concrete mixing truck under full load B/hg (B- horizontal distance between the barycenter and the rear axle axis, hg - height of barycenter) shall be less than 0.7. Lateral Stability (F-T) / hg (T- horizontal distance between the barycenter and longitudinal center level, F = (A2 (Z-B) + A1B) /2Z, A1-front gauge, A2-rear track Z-wheelbase) shall be not less than 0.5.
06-11 Hydraulic System
Truck crane, all terrain crane shall comply with the requirements of JB 8716 “Truck crane and wheel crane --Safety code”; Aerial working vehicle shall comply with the requirements of Article 8 of JG 5099 “Safety rules for aerial work machinery”; hydraulic pressure system of the special structure vehicle shall be equipped with the safety devices preventing overload and hydraulic shock. Leakage and crack are not allowed. The set pressure of the overflow valve shall be not more than 110% of system nominal working pressure. Operating persistently under nominal working pressure for 2 hours, the maximum temperature of hydraulic oil tank shall not exceed 80°C. When hydraulic line is damaged or hydraulic pressure system pressure hydraulic system loses pressure, oil cylinder playing a supportive role tanks shall be able to lock automatically.
06-12 Lifting Hook
Truck crane, all terrain crane shall comply with the requirements of JB 8716 “Truck crane and wheel crane --Safety code”.
06-13 Steel Cable
Truck crane, all terrain crane shall comply with the requirements of JB 8716 “Truck crane and wheel crane --Safety code”; Aerial working vehicle shall comply with the requirements of JG 5099 “Safety rules for aerial work machinery”; The steel cable of truck with loading crane and wrecker vehicle shall be arranged neatly on the reel. The steel cable shall not be messed up, and shall not knot or twist while lifting.
06-14 Brake
The hoisting and rotary mechanism of the crane truck and the truck with loading crane shall be equipped with gear brakes. The gear brake of the hoisting machine must be of normally closed type with assurance factor of no less than 1.5.
06-15 Hoisting, Amplitude Varying, Stretching and Rotating Mechanism
Truck crane, all terrain crane shall comply with the requirements of JB 8716 “Truck crane and wheel crane --Safety code”; Boom of wrecker vehicles shall be smooth and accurate without creeping, shock or strike while stretching, amplitude varying and rotating. The boom movement must not interfere or be interfered by the movement of other components in the course of the operation. It shall be guaranteed that the boom does not slide while hoisting with full load after a stop in the air during lifting operation.
06-16 Manometer
For the special purpose vehicle which must be equipped with manometer, the accuracy of the manometer shall be no lower than 1.6.
06-17 Structure Strength
Aerial working vehicle shall comply with the requirements of JG 5099 “Safety rules for aerial work machinery”; Truck crane shall comply with the requirements of GB/T 6068 “Test code for truck crane and mobile crane”; All terrain crane shall comply with the requirements of GB/T 27996 “All terrain crane”; Truck with loading crane shall comply with the requirements of QC/T 459 “Truck with loading crane”; Truck mounted concrete pump shall comply with the requirements of QC/T 718 “Truck mounted concrete pump”. The overload protection device installed on the vehicle shall not have any artificial device failure. The load value for strength test shall be ultimate load to enable lifting in operating mode. When the special vehicles are under rated load, the stress value of the main structure shall be less than the permissible stress value.
06-18 Control Cab
Truck crane, all terrain crane shall comply with the requirements of JB 8716 “Truck crane and wheel crane --Safety code”.
06-19 Emissions
The vehicle engine emissions shall comply with the requirements of GB 20891”Limits and measurement methods for exhaust pollutants from diesel engines of non-road mobile machinery”. For suck type and suck-sweeping type road sweeper, the average dust intensity at the outlet of the dust absorption system shall not be greater than 60mg/m3.
06-20 Hydraulic Hose
Aerial working vehicle shall comply with the requirements of JG 5099 “Safety rules for aerial work machinery”; bursting strength of hydraulic hose shall comply with the requirements of JG 5099 “Safety rules for aerial work machinery”.
When adopting new design and new technique on whole vehicle or related system, spare parts due to technology updating, manufacturer shall provide the verification results as a proof of the conformity of vehicle with safety standards to certification body for determination. The determination of standard conformity for major security, environmental protection projects, shall comply with relevant announcement or decision by CNCA.
Appendix 2: Definition of Vehicle Category, Variant and Version
1. Category M1:
A “category” shall consist of vehicles which do not differ in at least the following essential respects:
-
Manufacturer
-
Manufacturer’s type designation
-
Essential aspects of construction and design:
-
Chassis/floor pan (obvious and fundamental differences)
-
Power plant (internal combustion/electric/hybrid)
“Variant” of a type means vehicles within a type which do not differ in at least the following essential respects:
-
Factory
-
Body style (e.g. saloon, hatchback, coupé, convertible, station-wagon, multi-purpose vehicle)
-
Power plant
-
working principle (positive ignition/compression ignition, four stroke/two stroke)
-
Number and arrangement of cylinders
-
Power differences of more than 30% (the highest is more than 1, 3 times the lowest)
-
Capacity differences of more than 20 % (the highest is more than 1, 2 times the lowest)
-
Powered axles (number, position, interconnection)
-
Steered axles (number and position)
“Version” of a variant means vehicles which consist of a combination of items approved to compose the same model, and of which system design and control device have no great impact on emission, fuel consumption and noise and having no differences in the following parameters:
-
Technically permissible maximum laden mass
-
Engine capacity
-
Maximum net power
-
Type of gearbox and number of gears
-
Maximum number of seating positions
2. Category M2 and M3
A “category” shall consist of vehicles which do not differ in at least the following essential respects:
-
Manufacturer
-
Manufacturer’s type designation
-
Type
-
Essential aspects of construction and design:
-
Chassis/self, Supporting body, Single/double deck, Rigid/articulated (obvious and fundamental differences)
-
Number of axles
-
Power plant (internal combustion/electric/hybrid)
“Variant” of a type means vehicles within a type which do not differ in at least the following essential respects:
-
Factory
-
Class as definition of “buses and coaches” (only for complete vehicles),
-
Extent of build (e.g. complete/incomplete)
-
Power plant
-
Working principle (positive ignition/compression ignition, four stroke/two stroke)
-
Number and arrangement of cylinders
-
Power differences of more than 50 % (the highest is more than 1, 5 times the lowest)
-
Capacity differences of more than 50 % (the highest is more than 1, 5 times the lowest)
-
Location (front, mid, rear)
-
Technically permissible maximum laden mass differences of more than 20 % (the highest is more than 1, 2 times the lowest)
-
Powered axles (number, position, interconnection)
-
Steered axles (number and position)
“Version” of a variant means vehicles which consist of a combination of items approved to compose the same model, and of which system design and control device have no great impact on emission, fuel consumption and noise.
3. Category N1, N2 and N3.
A “category” shall consist of vehicles, which do not differ in at least the following essential respects:
-
Manufacturer
-
Manufacturer’s type designation
-
Type
-
Essential aspects of construction and design
-
Chassis/floor pan (obvious and fundamental differences)
-
Number of axles
-
Power plant (internal combustion/electric/hybrid)
“Variant” of a type means vehicles within a type which do not differ in at least the following essential respects:
-
Factory
-
Body structural concept (e.g. platform truck/tipper/tanker/semi-trailer towing vehicle) (only for complete vehicles)
-
Extent of build (e.g. complete/incomplete)
-
Power plant
-
Working principle (positive ignition/compression ignition, four stroke/two stroke)
-
Number and arrangement of cylinders
-
Power differences of more than 50 % (the highest is more than 1, 5 times the lowest)
-
Capacity differences of more than 50 % (the highest is more than 1, 5 times the lowest)
-
Technically permissible maximum laden mass differences of more than 20 % (the highest is more than 1, 2 times the lowest)
-
Powered axles (number, position, interconnection)